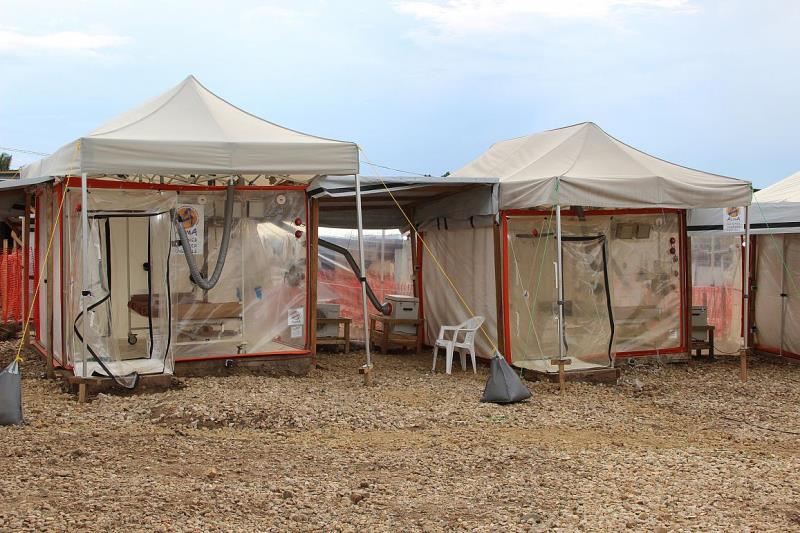
The results from a clinical study carried out in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) have demonstrated that investigational drugs reduce death risk from Ebola virus disease (EVD).
Investigational therapeutics mAb114 and REGN-EB3 performed better compared to investigational treatment ZMapp. However, drug remdesivir performed similar to ZMapp.
ZMapp monoclonal antibody cocktail has been developed by Mapp Biopharmaceutical.
The new data from the NIH-DRC-WHO trial also demonstrated that early diagnosis and treatment are associated with an increased likelihood of survival from EVD.
In August, the study leaders halted the study based on the recommendation of an independent data and safety monitoring board after evaluating preliminary data from 499 study patients.
The latest data offers a comprehensive analysis of the full dataset from around 200 additional patients recruited in the study.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataA consortium coordinated by the World Health Organisation (WHO) has conducted the Pamoja Tulinde Maisha (PALM) clinical trial.
Between November 2018 and August 2019, the trial recruited 681 people with EVD at four Ebola treatment centres (ETCs) in the cities of Beni, Butembo, Katwa and Mangina.
The trial compared mortality among patients who received one of three investigational Ebola drugs from a control group of patients who received the investigational monoclonal antibody cocktail ZMapp.
The investigators found a mortality rate of 19% among patients arriving at the ETC within one day of reported onset of symptoms.
Patients arriving after five days of symptoms had a mortality rate of 47%.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases’ (NIAID) Vaccine Research Center developed the mAb114 single monoclonal antibody product and licensed it to Ridgeback Biotherapeutics and Mapp Biopharmaceutical.
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals developed the REGN-EB3 monoclonal antibody and Gilead Sciences developed the remdesivir antiviral drug. The four therapies have been administered as intravenous infusions.
NIAID clinical research and special projects deputy director Dr Clifford Lane said: “Despite unprecedented challenges, including an unstable electrical power grid and evacuations of staff and patients from treatment centres due to violent attacks, the PALM trial demonstrates that scientifically rigorous and ethically sound clinical research can be conducted during disease outbreaks.”