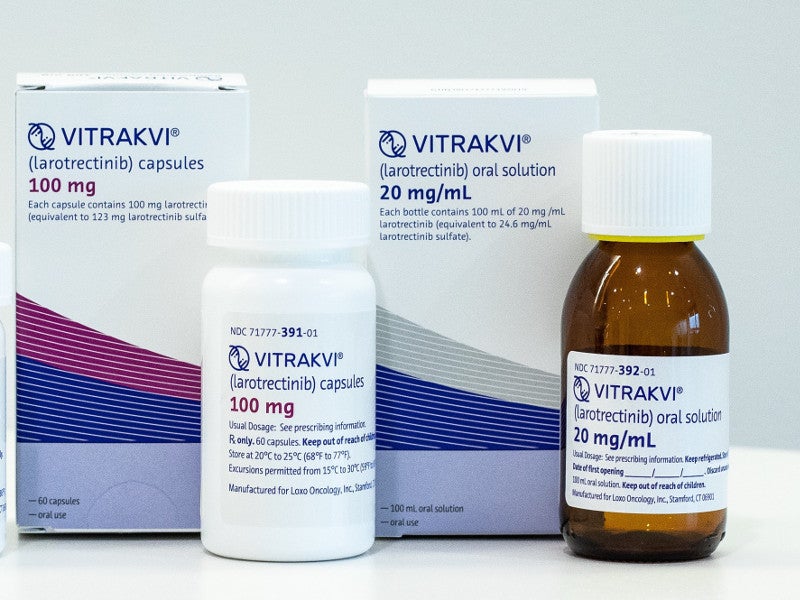
Vitrakvi® (larotrectinib) is an oral tyrosine kinase (TRK) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of advanced solid tumours in adult and paediatric patients with neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion.
The drug was developed by Bayer and Loxo Oncology in a partnership formed in November 2017. It is one of the first TRK inhibitors approved for its indication.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation, rare paediatric disease designation and orphan drug designation for the drug.
Bayer and Loxo Oncology submitted a new drug application for larotrectinib to the FDA in March 2018. The application was accepted and granted priority review status in May 2018. Vitrakvi was approved by the FDA in November 2018.
Bayer also submitted a marketing authorisation application for the drug to the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in August 2018.
Causes and symptoms of solid tumours with NTRK gene fusion
The NTRK gene is a crucial component for normal cell growth and proliferation. The gene fuses with an unrelated gene due to genomic alterations, resulting in the formation of an altered TRK protein.
TRK fusion proteins are known to promote tumour cell development and are found in various solid tumours. TRK fusion cancers are rare but can occur in any part of the body, including the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system and soft tissues.
Common symptoms of solid tumours include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, easy bruising, bleeding from any part of the body, and change in disposition.
Vitrakvi mechanism of action
Vitrakvi is an oral TRK inhibitor claimed to be effective in inhibiting tropomyosin receptor kinases A, B and C in purified enzyme assay panels encoded by NTRK I, II and III genes.
The drug has also shown anti-tumour activity during in-vitro and in-vivo tumour models.
Vitrakvi is available in the form of capsules and an oral solution. The hard gelatin capsules are available in 25mg or 100mg strength. They are composed of gelatine, titanium dioxide and edible ink.
The oral solution contains 20mg / ml larotrectinib.
Clinical trials on Vitrakvi
The FDA’s approval of Vitrakvi was based on positive pooled study results from three multi-centre, open-label, single-arm clinical trials, LOXO-TRK-14001 (NCT02122913), SCOUT (NCT02637687) and NAVIGATE (NCT02576431).
The studies’ primary endpoints were the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR).
LOXO-TRK-14001 is a Phase I clinical trial that enrolled 90 patients with advanced solid tumours and NTRK1, NTRK2 or NTRK3 gene fusion. The study is expected to be completed in April 2019.
The Phase I / II clinical trial SCOUT enrolled 112 paediatric patients with advanced solid or primary central nervous system tumours to determine the drug’s safety profile and ORR.
The Phase II non-randomised clinical trial NAVIGATE enrolled 176 patients with advanced solid tumours having NTRK1, NTRK2 or NTRK3 gene fusion to evaluate the ORR in patients.
SCOUT and NAVIGATE clinical trials are expected to be completed in December 2019.
Adult patients were administered a 100mg oral twice-daily dosage of Vitrakvi, while paediatric patients aged 18 years and younger received 100mg / m².
The efficacy assessment performed in the first 55 patients enrolled across all the clinical trials showed an ORR of 75%, including a complete response rate of 22% and a partial response rate of 53% in patients.
The most common adverse events reported in the trial were fatigue, nausea, dizziness, vomiting, increased aspartate aminotransferase, coughing, increased alanine aminotransferase, constipation and diarrhoea.