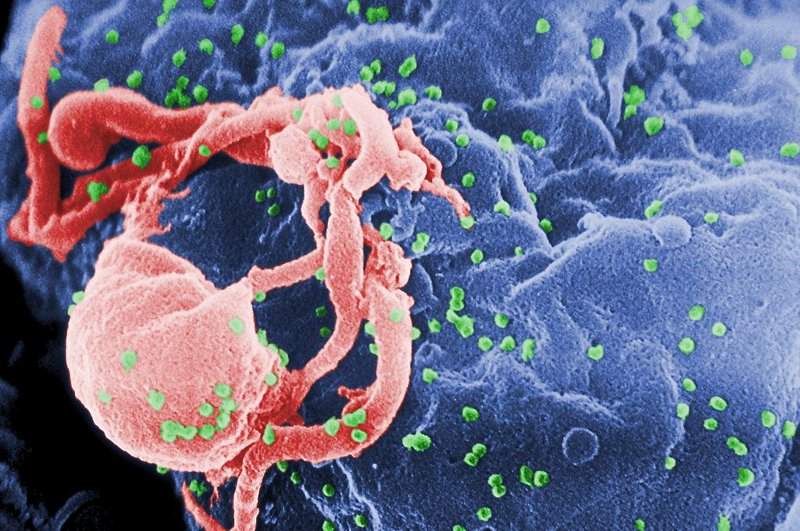

NIAID began HVTN 702 study of new HIV vaccine regimen in South Africa
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) initiated a new research study, HVTN 702, of a new HIV vaccine in South Africa.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
The vaccine regimen will test two experimental vaccines, a canarypox vector-based vaccine known as ALVAC-HIV and a two-component gp120 protein sub-unit vaccine with an adjuvant to improve the body’s immune response to the vaccine.
The vaccines are free from HIV and are therefore safe to be administered to the study subjects.
Eli Lilly and Company’s Phase III EXPEDITION3 trial of solanezumab failed to meet primary endpoint
Eli Lilly and Company reported that its Phase III EXPEDITION3 clinical trial of solanezumab failed to meet its primary endpoint in treating people with mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Lilly’s solanezumab is a phase III, humanised monoclonal IgG1 antibody developed against the mid-domain of the Aβ peptide.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe multinational, phase III EXPEDITION3 trial has examined more than 2,100 patients diagnosed with mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease.
Profectus began Phase I trial of VesiculoVax-vectored vaccine to treat Ebola

Profectus BioSciences began a Phase I trial of its VesiculoVax-vectored vaccine to treat Ebola.
Ebola is a filovirus that causes periodic outbreaks of a highly contagious and infectious human disease associated with severe hemorrhagic fever, with a mortality rate that ranges between 50% and 90%.
Transmitted from wild animals, the virus spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission.
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis began clinical trial of dantrolene to treat Wolfram syndrome

The Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis began a new clinical trial of the drug known as dantrolene to treat patients with Wolfram syndrome.
Wolfram syndrome is a genetic disorder where a patient develops diabetes at a premature age and requires insulin injections every day. The disease also results in hearing loss, vision problems and difficulty with balance.
Dantrolene is a muscle relaxant that works by restoring a normal level of calcium in the muscles, thereby reducing a rise in body temperature. It is indicated to treat cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis and muscle spasticity.
PROMISE study presented drug therapy to eliminate HIV transmission from breastfeeding mothers to infants
The Promoting Maternal and Infant Survival Everywhere (PROMISE) study conducted in sub-Saharan Africa and India stated that administration of a three-drug, anti-retroviral regimen during breastfeeding of HIV-infected mothers who have a strong immunity system eliminates the risk of HIV transmission by breast milk to their infants.
Multi-component study PROMISE involved 2,431 pairs of HIV-infected mothers and their HIV-uninfected infants from South Africa, Malawi, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe and India.
A component of this study was designed to determine ways to eliminate HIV transmission from HIV-infected women to their babies during pregnancy, delivery and after childbirth, while maintaining good health of both the mother and her baby.
Wellcome recommended clinical trial network for efficient and cheap drug development
UK-based biomedical research charity the Wellcome Trust released a report suggesting the creation of a clinical trial network to facilitate a cheap and efficient way of developing drugs for drug-resistant infections.
The network will address challenges faced during conducting researches to develop new antibiotics such as finding and involving 50 to 300 hospitals for every clinical trial.
Wellcome director Jeremy Farrar said: “We are entering a post-antibiotic era. Hundreds of thousands of people die every year from drug-resistant infections, and numbers are increasing at an alarming rate.
AstraZeneca and Microsoft collaborated to develop new drug technology for cancer
AstraZeneca collaborated with Microsoft to develop new technology for drug intervention for a personalised treatment of cancer.
As part of the collaboration, the companies will design a new computer modelling system that will signal pathways in cancer cells to predict the best place for the application of new drugs.
AstraZeneca bioinformatics, oncology, innovative medicines and early development (IMED) principal scientist and global strategy lead Jonathan Dry believes that the new system will decrease the wet lab work and can pave the way for an accelerated drug development.
Gradalis began dosing in Phase I breast cancer trial of Vigil EATCs and durvalumab

US-based clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company Gradalis dosed the first patient in its pilot Phase I trial of a combination of Vigil Engineered Autologous Tumour Cells (EATCs) and durvalumab to treat advanced breast cancer.
Vigil is an investigational, cellular immunotherapy technology based on a combination of genetic engineering concepts with the science of immuno-oncology to induce an immune response to cancer cells.
A patient’s tumour cells are engineered with a plasmid carrying the gene vector for shRNA Furin and GMCSF to issue a systemic, T-cell directed immune response administered to the patient through intradermal injections.
Boston Biomedical began Phase III CanStem303C study of napabucasin to treat colorectal cancer
Boston Biomedical dosed the first patient in CanStem303C, a new global Phase III study investigating napabucasin in combination with standard of care (FOLFIRI) in patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal carcinoma (mCRC).
Around 1.4 million patients are diagnosed with colorectal cancer every year, making the disease the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths annually, with almost 700,000 deaths reported worldwide.
An estimated 50% of all colorectal cancer patients will experience disease recurrence.
Tilray and University of British Columbia began Phase II trial of medical cannabis in Canada

Canadian-based medical cannabis producer Tilray and University of British Columbia began patient enrolment within Canada’s first Phase II clinical trial of medical cannabis to treat post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The cannabis plant belongs to the family of Cannabaceae of the nettle order, which is believed to be effective in soothing nausea, increase appetite, relieve pain and reduce epileptic seizures.
Claimed as one of the world’s first large-scale clinical trials, the Phase II, triple blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, crossover clinical trial is intended to determine the safety and efficacy of three potencies of medical cannabis to treat chronic, treatment-resistant PTSD symptoms as a result of a traumatic event.
Canada began first clinical study of Zika vaccine

Université Laval’s Infectious Disease Research Centre (IDRC) and Centre de recherche du CHU de Québec-Université Laval (CHU) jointly conducted the first clinical study for a Zika vaccine in Canada.
The Zika virus is carried by Aedes mosquitoes, which cause symptoms such as mild fever, skin rash, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise or headache that can last between two to seven days.
Infection of a pregnant woman can cause the fetus to develop microcephaly, an abnormal smallness of the head causing incomplete brain development.
ProMedica and Stemedica planned human stem cell trial for traumatic brain injury
US-based companies ProMedica and Stemedica Cell Technologies (Stemedica), along with the family of hockey legend Gordie Howe, planned to begin a human stem cell trial to advance the treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI).
The three-year study, known as Gordie Howe Initiative, will support clinical research and increase awareness about TBI with an initial focus on war veterans, athletes and automobile accident victims.
The first stage of the initiative will include a US-based Phase IIa clinical trial to evaluate preliminary safety and efficacy of Stemedica’s proprietary allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), in patients with moderate-to-severe TBI.





