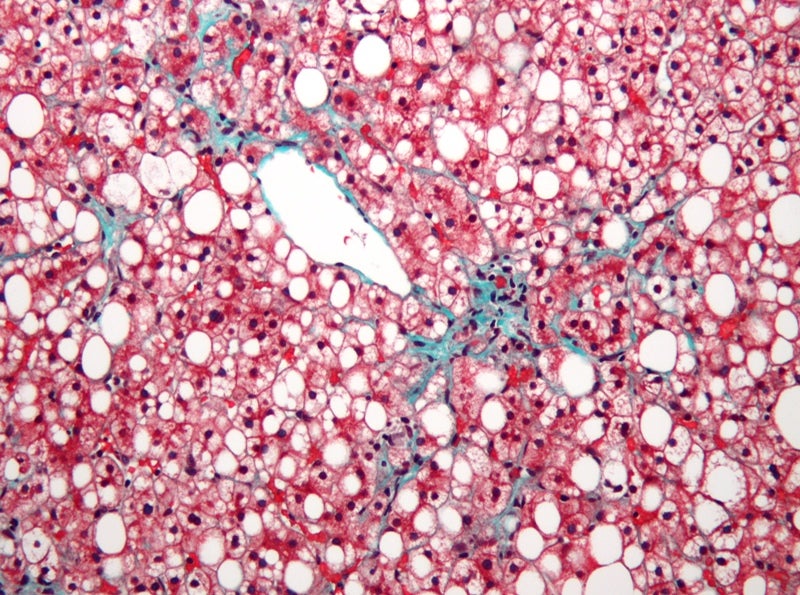
Second Genome has dosed the first patient in a Phase II clinical trial assessing SGM-1019 for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a subtype of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
SGM-1019 is an oral, small molecule inhibitor of the P2X7 receptor that can activate inflammasome, and mediate inflammation and fibrosis.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
The company intends to enrol 100 patients at sites across the US for the randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
The trial aims to investigate the preliminary safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of twice-daily dosing of oral SGM-1019 at two different dose levels.
It is expected to provide top-line data in the first half of next year.
The trial’s principal investigator Stephen Harrison said: “There are no approved therapies for NASH at this time, and, while there are many in development, SGM-1019 is directed at the inflammation underlying this condition.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData“We know that inhibiting P2X7 results in significant reduction in inflammation and fibrosis in preclinical models of disease and look forward to seeing the data from this study.
“SGM-1019 has the potential to provide a much-needed treatment option for the growing number of patients with NASH.”
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases suggests around 3% to 12% of the US population is affected by NASH.
The disease commonly attacks obese people or those who have other metabolic conditions, including type 2 diabetes or elevated lipids.





