The US National Eye Institute’s (NEI) eye institute (NEI) thas started a clinical study to investigate the natural history of early age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
The AMD Ryan Initiative Study (ARIS) will enrol 500 people over a period of five years across 20 sites in the US, UK, Australia, Germany, and Italy.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
It will use new technologies to visualise structures within the eye and measure their function.
Using new technologies, researchers aim to identify biomarkers of disease progression before it advances to late-stage disease and causes vision loss.
AMD is currently considered to be one of the major causes of vision impairment and blindness between people aged 50 and older in the US.
NEI deputy clinical director Emily Chew said: “The findings will contribute to our understanding of the underlying biology driving the transition from early to late-stage disease so that therapies can be developed to halt its progression.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData“Treatments that halt the disease at its early stage would have an enormous public health impact.”
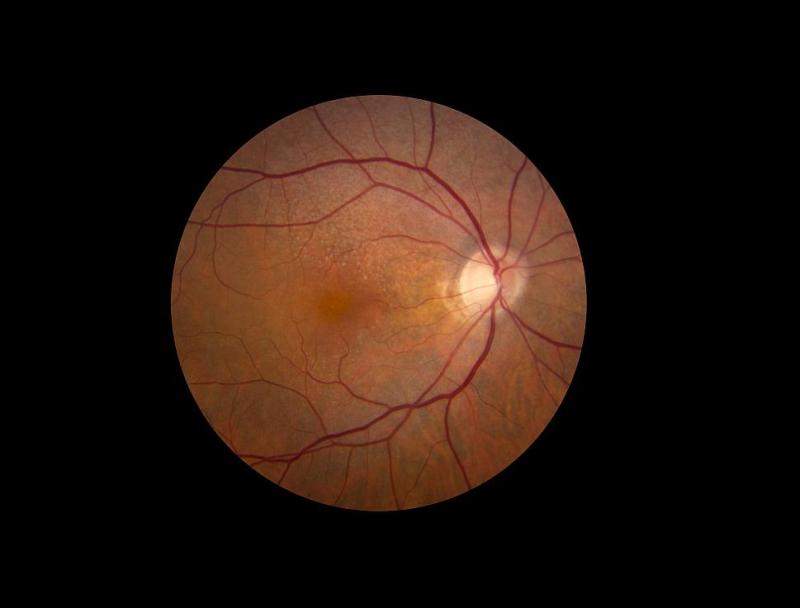
As part of the ARIS study, the eye health will be monitored of 200 people who have bilateral early AMD, defined by the presence of medium-size drusen, yellowish deposits that accumulate under the retina.
It will also add 200 people with early, reticular pseudodrusen, a type of lesion that causes the retina to have a giraffe-like macular pattern.
A further 100 age-matched, drusen-free control participants will also be included for comparison.
The study participants will go through routine spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT), a type of imaging that shows high-resolution, cross-sectional views of the retina and can detect small changes in the volume of drusen over time.
Participants’ visual function will also be calculated by dark-adapted fundus perimetry, a test that determines the sensitivity of light perception in specific parts of the retina after a person’s eyes have adapted to the dark.





