Hutchison China MediTech (Chi-Med) has initiated its Phase II study by administering the first dose of sulfatinib to treat second-line biliary tract cancer (BTC) patients in China.
Sulfatinib is an orally administered, angio-immunokinase inhibitor developed to selectively target vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R), the three key tyrosine kinase receptors considered responsible for tumour angiogenesis and immune evasion.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
The Phase II study is being conducted as a multi-centre, single-arm, open-label trial intended to test the safety and efficacy of sulfatinib as a monotherapy to treat advanced or metastatic BTC patients who failed one prior systemic therapy.
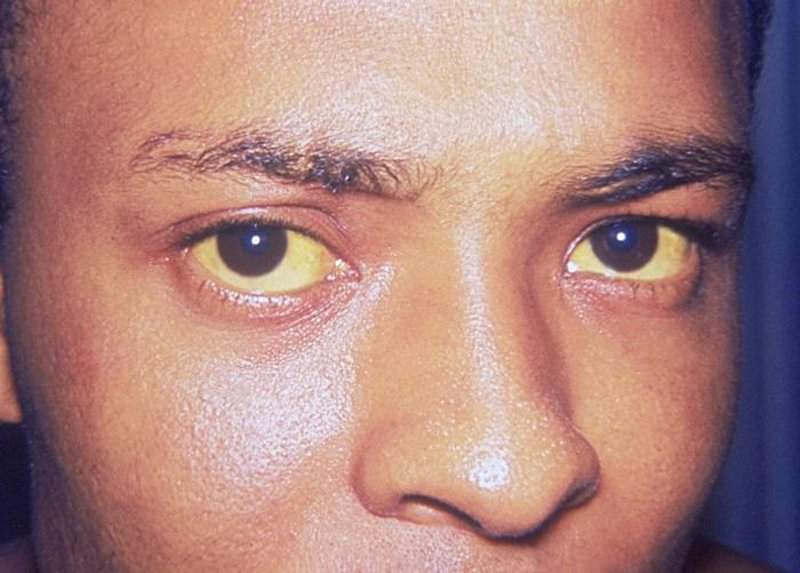
BTC, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare, fatal disease condition arising from the biliary tract epithelia, including intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. It is the second most frequently occurring type of liver cancer in the world.
The study’s primary endpoint is progression free survival (PFS) after administering sulfatinib for 16 weeks and its secondary endpoints are objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), duration of response, PFS, overall survival (OS) and safety.
In addition to the BTC trial, six sulfatinib clinical trials are underway in China and the US, including two Phase III studies known as SANET-p and SANET-ep and a Phase II study in thyroid cancer patients.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData




