Admelog® (insulin lispro) is a rapid-acting human insulin analogue approved as a follow-on product to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults and paediatric patients aged three years and older.
Discovered and developed by Sanofi-Aventis, Admelog received tentative approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in September 2015 and final approval in December 2017.
The drug has also received marketing authorisation approval (MAA) under the proprietary name Insulin lispro Sanofi from the European Commission (EC) in July 2017.
Diabetes causes and symptoms
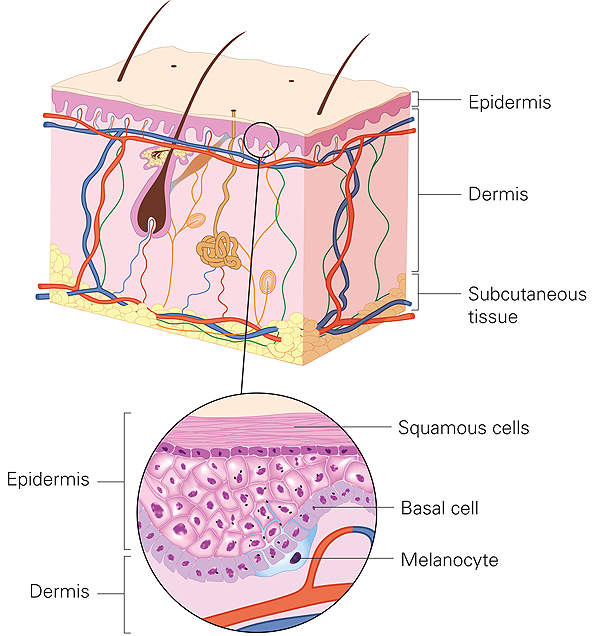
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterised by high levels of blood glucose in the body. It can lead to severe health problems such as heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, blindness and amputation if not treated or controlled properly.
Type 1 diabetes is caused when the body does not produce enough insulin, while type 2 diabetes occurs when the body is unable to properly use the produced insulin. Type 2 diabetes accounts for between 90% and 95% of all diabetes cases.
The symptoms of the disease include frequent urination and increased thirst and hunger.
An estimated 30 million people in the US are affected by diabetes, according to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
Admelog’s mechanism of action
Admelog contains a rapid-acting insulin product, which helps to control blood sugar levels in diabetics. It regulates glucose metabolism and lowers blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by the skeletal muscle and fat. It also inhibits hepatic glucose production.
The drug is available as insulin lispro injection 100ml and also comes in multiple-dose vials of 10ml and 3ml for single-patient use through SoloStar prefilled pens.
Admelog can be administered either as subcutaneous injection using an insulin pump or through intravenous infusion. It should be administered before a meal to control blood sugar levels after eating.
Clinical trials on Admelog
FDA approval for Admelog was provided through the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act 505(b)(2) pathway. A new drug application (NDA) was approved based on physicochemical, non-clinical and clinical similarities to insulin lispro product Humalog, which is already approved in the US.
The authorisation was also based on data obtained from a 26-week Phase III open-label, active-controlled clinical trial, which enrolled more than 1,000 adults living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The trial evaluated the glucose lowering effect of Admelog.
It enrolled 507 adult patients with type 1 diabetes and 505 adult patients with type 2 diabetes. The patients were randomised to either Admelog or Comparator (Humalog) by subcutaneous injection immediately prior to meals.
The results demonstrated that Admelog® provided a mean reduction in Haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), which was non-inferior to the one achieved with the comparator at week 26.
Another Phase III clinical trial was conducted on paediatric patients 12 years and older with type 1 diabetes. The one-year randomised, parallel, open-label, and active-controlled study enrolled 167 patients and compared the safety and efficacy of another insulin lispro product 100ml with those of regular human insulin 100ml.
A crossover clinical trial in paediatric patients aged three years and older was conducted for eight months. This study also compared 100ml of insulin lispro product with regular human insulin.
Results from both studies showed that insulin lispro achieved better glycaemic control when compared to regular human insulin as measured by HbA1c.
The most common adverse reactions found in the clinical studies were hypoglycaemia, itching, rash and injection site reactions.