Idelvion (Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Albumin Fusion Protein) is an injectable formulation developed by CSL Behring, for the treatment of haemophilia B in children and adults.
The biological license application (BLA) for Idelvion was submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration on 5 December 2014.
The European Medical Agency (EMA) approved the marketing authorisation application for Idelvion for the treatment of haemophilia B on 29 February 2016.
It was followed by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the same indication on 4 March 2016. Idelvion is also approved in Canada and under review by regulatory agencies in Australia, Switzerland and Japan.
Haemophilia B causes and symptoms
Haemophilia B is a genetically inherited bleeding disorder due to lack of blood clotting factor IX. It is usually caused by X-linked recessive trait with a defective gene located on the X-chromosome.
The disease is most commonly seen in males, because females have two X-chromosomes and if a defective gene is located on one X-chromosome, the gene on the other chromosome can make enough IX factor and help in blood clotting.
Whereas males have a single X-chromosome and if the defective gene is located on the X-chromosome, they cannot produce the blood factors resulting in the development of haemophilia B.
The main symptom of the disease is bleeding and the disease is usually associated with symptoms such as bleeding and swelling in joints, blood in urine or stool, bruising, haemorrhage in gastrointestinal tract or urinary tract, nasal bleeding, and prolonged and spontaneous bleeding from cuts, tooth extraction and surgery.
Idelvion’s mechanism of action
Idelvion is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, lyophilised powder to be reconstituted with sterile water for intravenous administration. It is available in 250IU, 500IU, 1,000IU or 2,000IU of Factor IX in single use vials.
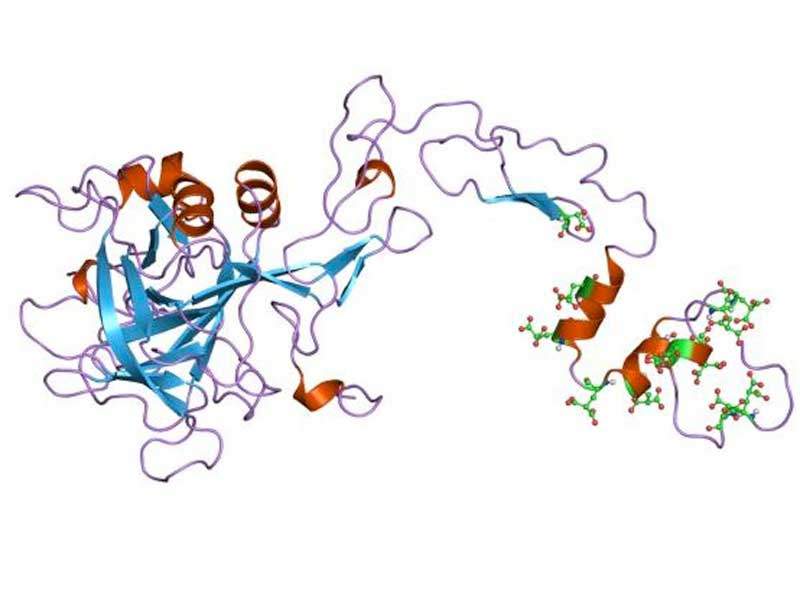
The active component of the drug is the recombinant human coagulation Factor IX albumin fusion protein, usually designated as rIX-FP. Once the drug is intravenously administered, the rIX-FP remains in the blood circulation until the Factor IX is activated. The albumin gets cleaved from Factor IX by releasing activated Factor IX during coagulation.
Clinical trials
The FDA, EMA and Health Canada approved Idelvion based on the results obtained from the phase three PROLONG-9FP clinical programme.
The programme included the first abstract reporting safety and efficacy results of the drug in previously treated adults with haemophilia B and the second abstract reporting safety and efficacy results of the drug in patients undergoing surgical procedures.
The first abstract includes two phase III trials, namely CSL654-3001 and CSL654-3002. The CSL654-3001 enrolled 63 patients of age group from 12 to 61, who were randomised to receive prophylaxis treatment once every seven days for six months or on-demand treatment for six months and then seven day prophylaxis treatment.
The trial CSL654-3002 enrolled 27 children of age group ranging from 1 to 11 years, who were randomised to receive seven-day prophylaxis treatment for 12 months. The overall annualised spontaneous bleeding rate in the trials was 0.00.
The extension study enrolled 76 patients from the phase III studies, who were continued on prophylaxis treatment and additional patients were put on long treatment intervals. A total of 50 patients experienced 100 exposure days without developing any inhibitor to factor IX or antibodies to rXL-FP.
The second abstract evaluated the safety and efficacy of rXL-FP in five major orthopaedic surgeries to prevent bleeding in four patients with haemophilia B. A median dose of 340IU/kg was given to the subjects prior to surgery and post surgery.
During all the procedures, none of the patients developed inhibitors to factor IX or antibodies to rXL-FP. No severe adverse reactions were reported during the trials and long-term tolerability was seen during the studies.