Quizartinib is an investigational oral selective FLT3 inhibitor being developed for the treatment of adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) that have a FLT3 internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutation.
The drug was originally discovered by Ambit Biosciences and later developed by Japanese pharmaceutical company Daiichi Sankyo, following the acquisition of Ambit Biosciences in 2014.
Quizartinib received breakthrough therapy designation from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August 2018. The FDA has also granted fast-track designation to the drug.
In addition, Quizartinib has received orphan drug designation from the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of AML.
Acute myeloid leukaemia causes and symptoms
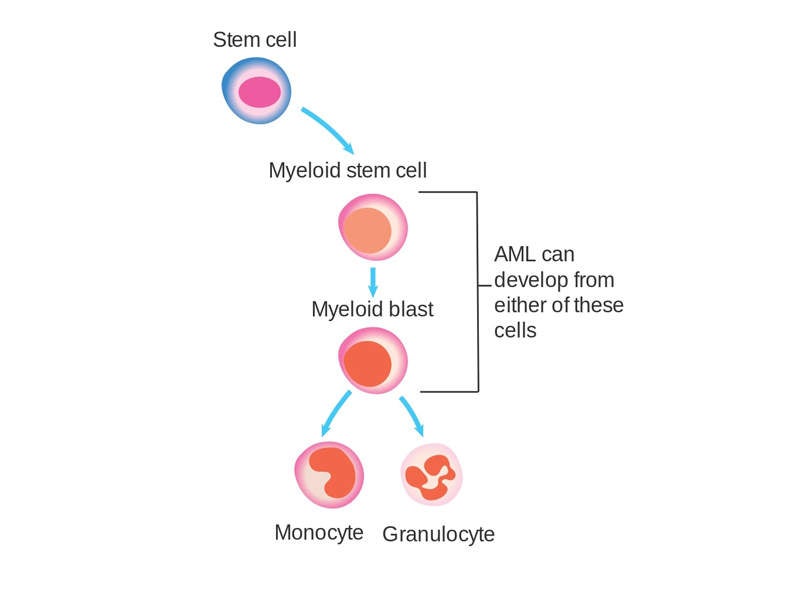
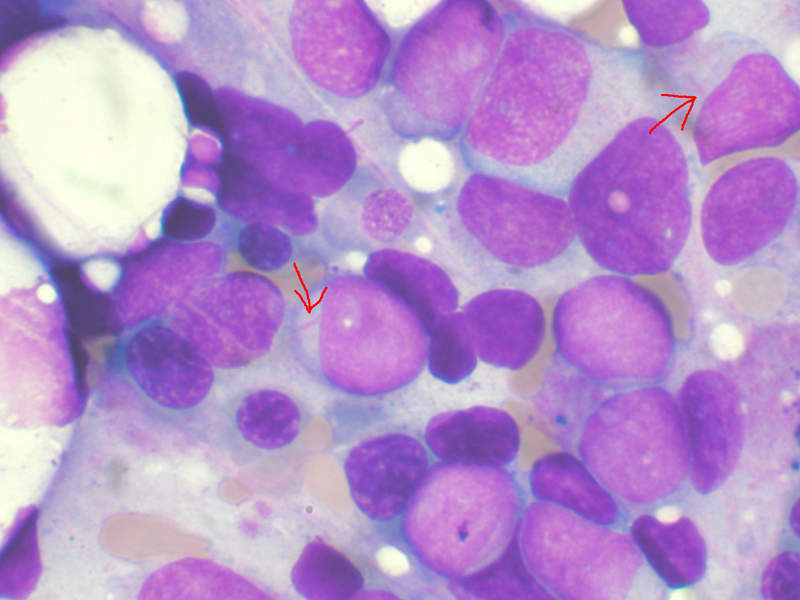
AML is an aggressive cancer of the blood and bone marrow that causes uncontrolled growth and spread of cancerous cells in various parts of the body. The malfunctioning white blood cells accumulate and interfere with the production of healthy blood cells.
An estimated 30% of AML patients carry a genetic mutation in the FLT3 gene called FLT3-ITD, which affects one in four patients with AML. FLT3-ITD AML is an aggressive form of the disease with a poor prognosis. No approved targeted therapies currently exist, as it is a difficult-to-treat disease with high risk of relapse.
Some of the general symptoms of AML include weight loss, fever, fatigue, swollen gums, bruising, bleeding and loss of appetite.
Quizartinib mechanism of action
Quizartinib is a once-daily, oral, small molecule FLT3 inhibitor that selectively binds to FLT3 tyrosine kinase receptor isoform.
This binding leads to the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and causes cancer cell death.
Clinical trials on Quizartinib
Daiichi Sankyo is being investigated in pivotal, global, open-label randomised, Phase III clinical trial QuANTUM-R. The trial enrolled 367 patients with refractory/relapsed FLT3-ITD-mutated AML.
The patients were randomised to either oral Quizartinib or salvage chemotherapy in a 2:1 ratio. The primary endpoint of the study was an improvement in the overall survival (OS) of the patients, compared to salvage chemotherapy.
Quizartinib demonstrated improved overall survival compared to chemotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD AML. Those that received single-agent Quizartinib demonstrated a 24% reduction in the risk of death compared with salvage chemotherapy-treated patients.
The median overall survival of patients treated with Quizartinib was 6.2 months, compared with 4.7 months for those treated with salvage chemotherapy. Results from the QuANTUM-R trial will form the basis for regulatory submissions for the drug worldwide.
The most common adverse events observed in Quizartinib-treated patients in the trial were nausea, fatigue, pain, pyrexia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia and hypokalaemia.
Another Phase III study named QuANTUM-FIRST is currently underway, enroling newly diagnosed FLT3-ITD AML patients in the US, the EU and Japan. It is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to study Quizartinib in combination with chemotherapy and as a maintenance monotherapy in patients with newly-diagnosed FLT3-ITD+ AML.
The primary endpoint of the clinical trial is event-free survival.
Marketing commentary on Daiichi Sankyo
Daiichi Sankyo is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. The company develops and supplies innovative pharmaceutical products to address a wide range of unmet medical needs.
The company primarily focusses on the development of novel therapies in oncology and rare indications such as neurodegenerative conditions, heart ailments and kidney diseases.