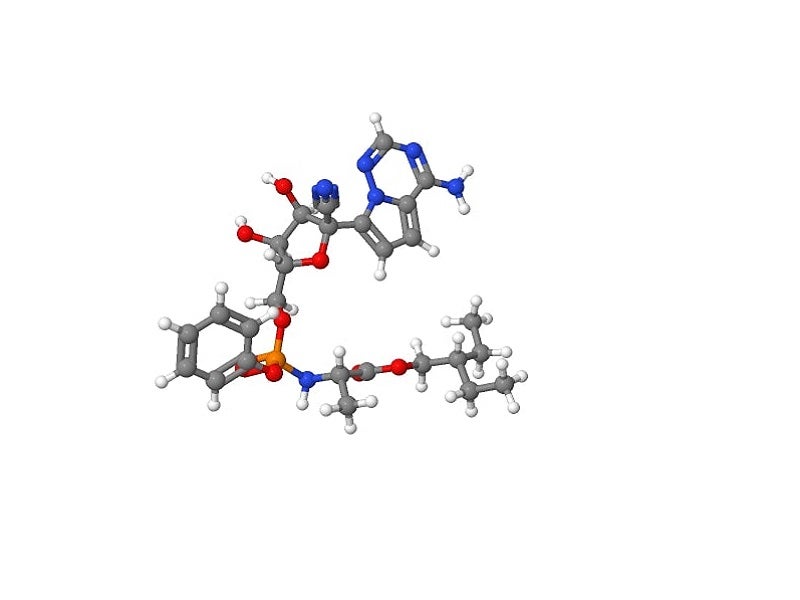
Remdesivir is an investigational antiviral drug being developed by Gilead Sciences for the treatment of Covid-19, a coronavirus disease, and Ebola virus infection.
The drug is currently not approved for any indication globally. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviewed the investigational new drug (IND) application filed by the company for remdesivir to treat COVID-19 and granted investigational new drug authorisation to study the drug in February 2020.
Gilead is working with government and non-government organisations and local regulatory agencies for providing remdesivir for compassionate use in eligible patients with COVID-19.
The drug is supplied as a stable lyophilised formulation for intravenous administration during clinical development.
COVID-19 causes and symptoms
Covid-19 is a disease caused by a novel human-infecting betacoronavirus. The coronavirus was identified in Wuhan city of Hubei Province in China, using next-generation sequencing and real-time RT-PCR, in December 2019.
The disease commonly spreads through respiratory droplets of the infected people. The primary symptoms of the disease are fever, cough and shortness of breath. The people infected with novel coronavirus mostly suffer from pneumonia.
Ebola virus infection causes and symptoms
Ebola virus infection is a fatal disease, which primarily originated on the African continent. The virus transmits from one to another through direct contact with body fluids and blood of infected people, contaminated objects, as well as infected animals such as fruit bats.
The most common symptoms of the disease are fever, body aches, fatigue, abdominal pain, diarrhoea vomiting, sudden bleeding and bruising.
Remdesivir mechanism of action
Remdesivir is a 1′-cyano-substituted adenosine nucleotide analogue with broad-spectrum antiviral activity against various RNA viruses. The compound undergoes a metabolic mechanism, activating nucleoside triphosphate metabolite for inhibiting viral RNA polymerases.
Clinical studies on Remdesivir for Covid-19 treatment
Gilead will initiate two Phase III, randomised, open-label, multi-centre clinical studies for the evaluation of safety and efficacy of remdesivir in patients with Covid-19 in March 2020. Approximately 1,000 infected individuals will be enrolled in the studies globally.
The patients will be intravenously administered with remdesivir, and the durations for two doses will be studied. Clinical improvement will be the main target of the study.
In one study, approximately 400 severe Covid-19 patients will be randomised to receive remdesivir for either five or ten days. In another study, 600 moderate Covid-19 patients will be randomised to receive remdesivir for five or ten days or standard-of-care alone.
The studies will be an extension to a few ongoing clinical studies on remdesivir. Two clinical studies led by the China-Japan Friendship Hospital are being conducted at multiple sites in the Hubei Province in China.
In one study, remdesivir is being evaluated in Covid-19 patients who showed severe clinical symptoms such as the need for supplemental oxygen. In another study, the drug is being tested in those hospitalised patients who are not showing significant clinical manifestations. Study results are expected in April 2020.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), US initiated the first randomised, controlled clinical trial in hospitalised adult patients with Covid-19 to determine the safety and efficacy of remdesivir at the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) in Omaha, US, in February 2020.
Clinical studies on Remdesivir for Ebola virus infection
Remdesivir is currently in the phase II stage of the clinical development for the potential treatment of Ebola virus infection.
The drug is being studied in combination with Mapp BioPharmaceutical’s ZMapp™, Regeneron’s REGN-EB3 and NIH’s mAb114 in a multi-centre, multi-outbreak, randomised, controlled safety and efficacy clinical study, enrolling 1,500 participants.