Developed by AGI Therapeutics, Rezular (arverapamil) is an orally administered triple-action intestinal regulator indicated for the treatment of diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D).
In May 2009, Rezular (arverapamil) failed in Phase III development, where it underwent extensive evaluation in the ARDIS clinical trial programme in patients with IBS-D.
In September 2009, AGI announced that it plans to consider alternative uses of Rezular. The company believes that Rezular can prove effective in treating diarrhoea and non-diarrhoea related problems.
IBS – a therapeutic challenge
IBS is a common, but until recently poorly understood, disorder of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It is described as a functional disorder of the GI tract, in which there is no obvious underlying pathology.
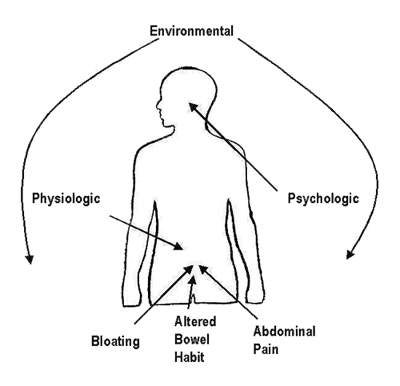
It is thought to arise from disturbances in GI motility and visceral sensory perception; visceral hyperalgesia, characterised by an increased conscious perception of abdominal pain, is common in patients with IBS. Patients with IBS can present with a variety of symptoms that can
include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Abdominal bloating or distension
- Faecal urgency
- Constipation, diarrhoea or both
IBS has proved notoriously difficult to diagnose and treat effectively. Until recently no drugs were specifically indicated for the treatment of IBS. Instead, patients would often seek over-the-counter (OTC) remedies to treat constipation, diarrhoea, abdominal pain and bloating associated with IBS.
Rezular – a new first-in-class drug for IBS-D
AGI Therapeutics, Rezular (arverapamil) is a single enantiomer moiety of racemic verapamil, a cardiovascular drug that has been in clinical use for 35 years.
However, in contrast to currently available commercial forms of racemic verapamil (a mixture of two enantiomers), arverapamil shows preferential activity in treating the symptoms of IBS-D without the traditional cardiovascular actions of the racemic drug. It combines affinity at L-type calcium channels with 5-HT2b and melatonin (MT1) receptor binding.
Gut function is controlled by both the enteric (intestinal) nervous system (ENS) and CNS, in which the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT) plays a fundamental role. Serotonin is present in large amounts in the ENS where it is involved in sensory, motor and secretory processes within the gut. It modulates gut motility and the perception of pain and also mediates intestinal secretion. Minor disturbances in serotonergic function can lead to symptoms of IBS described above.
Rezular’s efficacy for IBS-D
Evidence of the clinical efficacy of Rezular (arverapamil) has been demonstrated in a Phase II study, where it proved significantly better than placebo in terms of IBS symptom relief including relief of pain and abdominal discomfort. Significant improvements were also observed on the Bristol stool scale and in IBS-specific QoL domains.
Rezular (arverapamil) was well tolerated, with adverse events consistent with the known safety profile of racemic verapamil.
Phase III trials were taken up with patients already receiving treatment in the ARDIS-1 trial. In this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group the efficacy and safety of Rezular (arverapamil) was assessed in about 1,200 patients.
Three doses of Rezular (arverapamil) were compared with placebo over a 12-week treatment period.
The study revealed that the drug did not provide any significant relief to patients suffering from IBS symptoms. Following the results of the clinical study, AGI planned to stop its development in this indication.
Marketing commentary
Estimates suggest that worldwide as many as 100 million people suffer from IBS, of which IBS-D accounts for about a third of all cases. For many patients IBS is a chronic condition requiring long-term treatment. Although not life-threatening, it can have a profound impact on peoples' quality of life.
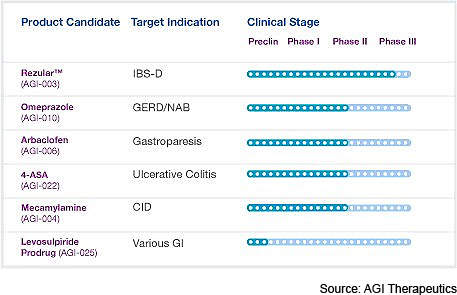
AGI Therapeutics specialises in the development of drugs for the treatment of GI disorders.