Siklos® is an orally administered tablet form of hydroxyurea that is indicated for the treatment of sickle-cell anaemia in paediatric patients aged two years and older.
The drug was discovered and developed by ADDMEDICA, a medical product company based in France.
The firm submitted a new drug application (NDA) for Siklos® to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in July 2016. Siklos® was approved in December 2017 and is expected to be launched in the market in the next few months.
Siklos® received marketing authorisation (MA) approval in Europe in 2007 and the drug has also received orphan medicinal product designation in the EU.
ADDMEDICA has partnered with Medunik USA to market Siklos® in the US.
Sickle cell disease causes and symptoms
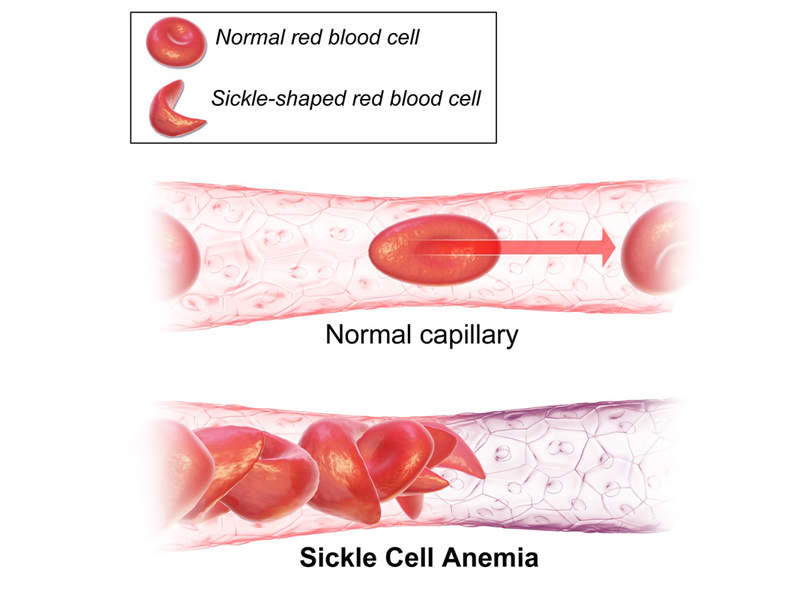
Sickle-cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disease affecting red blood cells (RBC).
Also known as sickle-cell anaemia (SCA) or drepanocytosis, this rare hereditary blood disorder is caused by a genetic mutation in the beta-chain of haemoglobin, which results in the formation of abnormal haemoglobin molecules called haemoglobin S (haemoglobin sickle). The molecules can distort the red blood cells into stiff and sickle-shaped cells.
Two other common forms of SCD are Haemoglobin SCD and haemoglobin Sβ thalassemia.
The disease can lead to painful swelling of the hands and feet, fatigue and jaundice, although the symptoms vary from person to person.
SCD is life-threatening in some cases, especially in case of acute chest syndrome.
Siklos’ mechanism of action
The hydroxyurea in Siklos® prevents deoxy-ribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis through the inhibition of the ribonucleotide reductase enzyme.
The drug also increases the concentration of foetal haemoglobin (HbF) and water content in red blood cells, as well as decreases neutrophils.
The drug is available in film-coated tablet form in 100mg and 1,000mg doses.
Clinical trial on Siklos
The US FDA approved Siklos® based on results obtained from an open-label, single-arm trial named European sickle cell disease cohort study Hydroxyurea (ESCORT-HU).
The study enrolled 405 paediatric sickle cell disease patients aged between two and 18 years. Of the total, 141 patients had not been treated previously with hydroxyurea.
The randomised patients had at least 12 months follow-up of the treatment. The study results demonstrated that patients administered with Siklos® had an increase in HbF levels.
The most common adverse reactions found in more than 10% of patients during the clinical studies were infections and neutropenia.
The side effects of Siklos® include fever, headache, skin problem, gastrointestinal problems and reduction in the count of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Marketing commentary on ADDMEDICA
Founded in 2005, ADDMEDICA is a medical company specialising in the discovery of innovative medicines for unmet medical needs.
ADDMEDICA’s product line includes investigational drugs in the therapeutic areas of haematology and wound healing. The company’s product line includes LUMIDERM® 6000 and LIQUIBAND® for wound healing and repairs.
The company also markets and distributes medical devices in the domain of organ grafts and lung transplantation.