Surfaxin (Lucinactant) is a non-pyrogenic pulmonary surfactant used for the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in premature infants. It is developed and produced by Discovery Labs.
In March 2012, surfaxin received US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in premature infants.
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) breathing disorder in premature infants
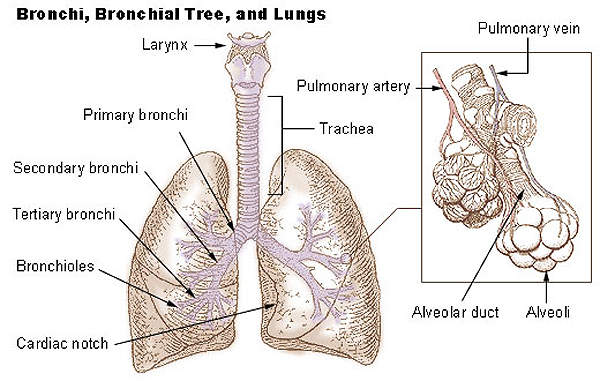
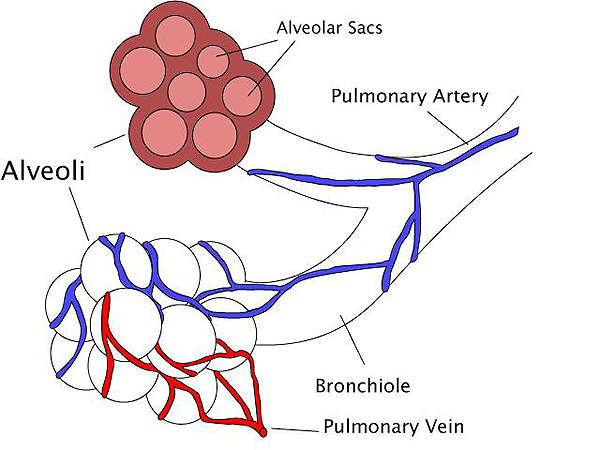
Respiratory distress syndrome is a breathing disorder which commonly affects the lungs of premature new born infants. It is caused when the lungs of new born infants have smaller amounts of pulmonary surfactant.
The surfactant is a liquid coat present inside the lungs which is essential for new born children to breathe-in air. Smaller amounts of surfactant lead to lack of oxygen and can subsequently damage the brain and other organs of the infant.
The disease affects more than 90,000 premature infants in the US alone.
Mechanism of action of the RDS prevention drug surfaxin
The drug contains a synthetic, peptide-containing endogenous pulmonary surfactant which lowers the surface tension at air-liquid interface of the alveolar surfaces during respiration. It works by compensating the deficiency of surfactant and reinstating surface activity of the lungs in the RDS-affected infants.
Clinical phase trials conducted on lucinactant by Discovery Labs
Discovery Labs conducted Phase I / II clinical trials on lucinactant between January 2000 and December 2003. The study enrolled 22 patients in the US. The primary outcome measure of the study was finding the number and type of adverse events.
The secondary outcome measures included assessment of pulmonary inflammatory markers, finding number of days on mechanical ventilation and chronic respiratory morbidity.
Phase II clinical trials on surfaxin were conducted from June 2007 to May 2010. It was a randomised, double-blind and parallel assignment which enrolled 165 patients. The primary outcome measure of the study was finding the safety and efficacy of the drug. Secondary outcome measures included finding ventilator-free days and oxygenation measurements through 48 hours after treatment.
FDA approval for surfaxin was based on a pivotal Phase III clinical trial known as SELECT (Safety and Effectiveness of Lucinactant vs. Exosurf in a Clinical Trial). It was a randomised, multicentre, double-blind, multidose study which enrolled 1,294 premature infants across Latin America and Europe.
Infants enrolled for the study weighed between 600gm and 1,250gm and were 32 weeks or less in gestational age. The infants were randomly dosed with one of three surfactants – surfaxin 5.8mL per kg, colfosceril palmitate 5.0mL per kg (exosurf) or beractant 4.0mL per kg (Survanta).
Results of the study showed that the infants in the surfaxin group demonstrated statistically significant improvements compared to colfosceril group. RDS at 24 hours with surfaxin was 39%, whereas in the colfosceril group it was 47%. RDS-related mortality through day 14 of surfaxin was five percent, whereas it was nine percent in colfosceril group.
Another Phase III clinical trial known as STAR (surfaxin therapy against RDS) evaluated the clinical safety and efficacy of the drug. It was a multinational, multicentre and supportive clinical trial. It enrolled 252 patients. It compared surfaxin with Curosurf, a leading animal-derived surfactant.
The most common adverse reaction found in the surfaxin group during the study included endotracheal tube reflux, pallor, endotracheal tube obstruction and the need for dose interruption.
Marketing commentary for surfaxin and other RDS drugs worldwide
The drug will be commercially available in US markets by the end of 2012. Discovery Labs holds the commercial rights of surfaxin in Central America, South America and other key European markets, while its partner del Dr. Esteve (Esteve) holds the marketing rights in Southern European markets.
The other surfactants approved by the FDA for the same indication include curosurf (poractant alfa), survanta (beractant), exosurf (colfosceril palmitate) and Infasurf (calfactant).