Volasertib (BI 6727) is a selective and potent polo-like kinase (Plk) inhibitor, currently being investigated for the treatment of patients with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
The drug is being developed by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals.
The new drug application (NDA) for Volasertib was submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012. The FDA granted breakthrough therapy designation for Volasertib in September 2013, for the treatment of AML patients who are aged 65 or older and have not received any treatment previously.
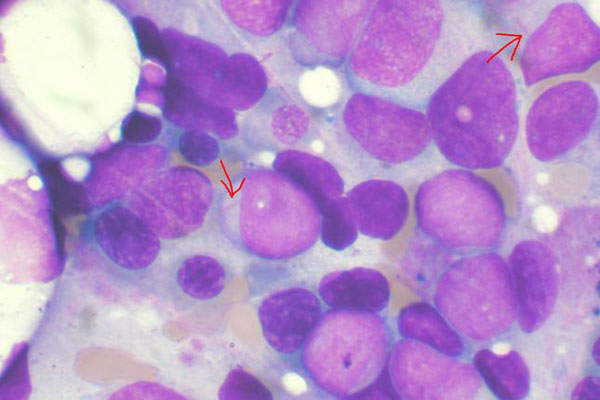
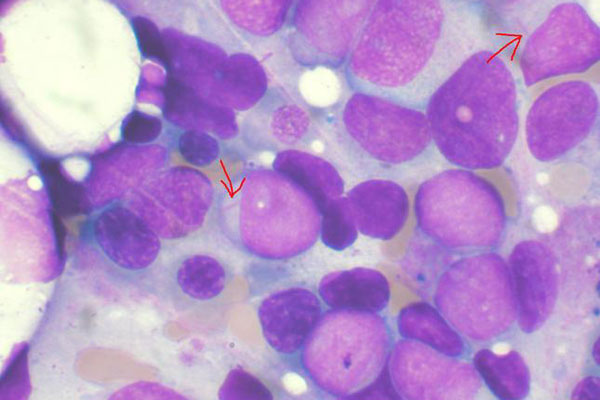
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML)
Leukaemia is a rare cancer that originates in the bone marrow and blood. Acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) is a common type of blood cancer with the lowest survival rates. AML commonly affects older people who are more than 65 years of age.
AML constitutes about 25% of all the adult leukaemia cases in the Western world. It is estimated that about 14,590 new cases of AML are diagnosed in the US every year, while 10,370 people die due to the disease.
Volasertib’s mechanism of action
Volasertib contains a polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitor. The drug belongs to dihydropteridinone derivatives, which work against cancer agents. The drug stops cell division by binding to the ATP-binding pocket of the PLK1 protein.
Volasertib will be available in tablet form for oral administration.
Clinical trials on Boehringer’s Volasertib
Boehringer Ingelheim conducted Phase I clinical trials on Volasertib between June 2010 and November 2010. The trial was a non-randomised, open label, single group, pharmacokinetics study. It enrolled seven patients with histologically or cytologically confirmed diagnosis of advanced, non resectable or metastatic solid tumour.
The primary outcome measure of the study was individual time course profiles of 14C-radioactivity in nmol/L in whole blood, plasma and urine and in nmol/kg for faeces in three weeks.
Secondary outcome measures included number of participants with adverse events as a measure of safety, plus assessment of preliminary therapeutic effects.
The FDA’s breakthrough therapy designation for Volasertib was based on the results of a Phase II clinical trial which compared Volasertib in combination with the established therapy of low-dose cytarabine (LDAC) versus LDAC alone.
The primary endpoint of the study was finding the objective response. The secondary endpoints included the event-free survival (EFS), overall survival (OS) and safety.
Results of the study showed that the objective response was observed in 31% of patients treated with the combination of Volasertib plus LDAC compared to 13.3% of the patients treated with LDAC alone.
The median event-free survival was 5.6 months in patients treated with the combination of Volasertib plus LDAC, compared to 2.3 months in patients treated with LDAC alone.
These encouraging results from the Phase II clinical study on Volasertib led to the initiation of the Phase III study, known as POLO-AML-2 study.
Boehringer Ingelheim initiated this clinical study on Volasertib in January 2013. It was a randomised, double blind, controlled, parallel assignment. It enrolled 660 patients aged above 65 years. The study is expected to be completed by April 2016.
The primary outcome measure of the study is the complete remission (CR), event-free survival (EFS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) in four years. Secondary outcome measures include the overall survival (OS), event-free survival (EFS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) in four years.
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals’ marketing commentary
Volasertib will be marketed by Boehringer Ingelheim in the US. Other drugs approved for the treatment of the same indication include Elacytarabine developed by Clavis Pharma and Synribo manufactured by Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
Related content
Elacytarabine (CP-4055) for Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukaemia, US
Elacytarabine (CP-4055) is a lipid-conjugated version of cytarabine, an anti-cancer agent drug approved for the treatment of blood-related cancers or haematological malignancies, commonly used to treat patients with leukaemia.
Bosulif (bosutinib) – Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia (CML) Treatment, US
Bosulif (bosutinib) is an investigational drug indicated for treating Philadelphia chromosome positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia (Ph+ CML).