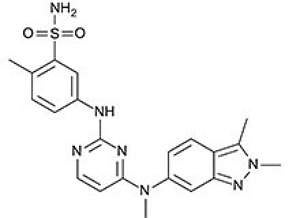
GlaxoSmithKline’s (GSK’s) Votrient is an approved medication for the treatment of renal cell cancer (RCC). The RRC treatment drug has conditional marketing authorisation in the European Union (EU).
In April 2012, votrient received approval for a second indication from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Votrient can now be administered for the treatment of certain subtypes of soft tissue sarcoma (STS) in patients who have received chemotherapy.
Votrient also received a positive opinion from the EU in May 2012 for the treatment of STS.
A study called PISCES (pazopanib versus sunitinib patient preference study in treatment-naïve metastatic renal cell carcinoma) was conducted to understand the patient preference of votrient versus another RCC drug, called Sutent (generic name: sunitinib). The results of the study, announced in June 2012, showed that 70% of patients preferred votrient, compared to 22% who chose sunitinib.
Renal cell cancer and soft tissue sarcoma
RCC is a type of kidney cancer affecting the inner lining of the kidney. It mostly affects adult men aged between 50 and 60 years. RCC can easily spread to other organs of the body, including the lungs.
Surgery and thermal ablation are the most common forms of treatment for small tumours. Targeted therapies, such as votrient, are gaining acceptance as clinical trials are establishing their effectiveness.
STS is a more aggressive form of cancer which affects the connective tissues of the body. There are nearly 20 types of STS that can affect the human body. STS can continue to affect the body if left untreated and can also affect other organs of the body, including the lungs and bones.
The National Cancer Institute estimates that nearly 11,000 people in the US were diagnosed with STS in 2011, of which approximately 4,000 died.
Votrient’s mechanism of action
Votrient is a multityrosine kinase inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor. It is a targeted therapy that contains pazopanib as the active ingredient.
The drug blocks the growth of tumour cells in several ways. It works by blocking proteins, such as tyrosine kinases, located on the surface of cancer cells and other targets within the cell. These proteins and targets are responsible for angiogenesis or production of new blood vessels in the cancer cells. By blocking these targets, votrient helps to destroy the cancer cells.
Clinical trials of votrient on patients with RCC
Related project
Sutent (Sunitinib Malate) – Treatment for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours, US
Sutent (sunitinib malate) is an oral multikinase inhibitor which is indicated for the treatment of progressive, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (NET).
A Phase II study on advanced RCC included the VEG102616 trial, which tested the safety and efficacy of votrient. The trial recruited 255 patients and demonstrated that the overall response rate (ORR) in patients was 35%. The data from this study supported Phase III trials of votrient.
The safety and efficacy of votrient in RCC was also established in a Phase III trial, which recruited 435 patients with locally advanced and / or metastatic RCC. The trial, named VEG105192, compared votrient with a placebo, with progression-free survival (PFS) as the primary endpoint. The median PFS in the votrient group was 9.2 months, compared with 4.2 months in the placebo group.
An open-label extension trial of the VEG105192 recruited 73 patients with advanced RCC. The primary endpoint of the study was safety and tolerability.
A second Phase III trial of votrient in advanced RCC is being carried out in July 2012. It is named the COMPARZ (comparing the efficacy, safety and tolerability of pazopanib versus sunitinib) study. It will be completed by the second half of 2012 and will compare the safety and efficacy of votrient with sunitinib. A total of 1,053 patients have been recruited for the study.
Study of votrient for the treatment of STS
Approval of votrient for STS was based on the Phase III PALETTE (pazopanib explored in soft tissue sarcoma) study. The randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicentre trial recruited 369 patients with metastatic STS who had received chemotherapy treatment.
Votrient was compared with placebo in the trial. The study established that votrient was effective in significantly improving PFS in patients, compared to placebo. The median PFS was 4.6 months in the votrient group, compared to 1.6 months in the placebo group.
Marketing commentary on treatments for RCC
Approved medications available in the market for the treatment of RCC include Pfizer’s sutent (sunitinib), Bayer’s Nexavar (sorafenib), Wyeth’s Torisel (temsirolimus), Novartis’ Afinitor (everolimus) and Roche’s Avastin (bevacizumab).
Sutent was one of the first drugs to establish itself in the market and is also considered as the standard treatment for the treatment of RCC.
Results of the PISCES study indicate the positive patient preference towards votrient. Based on this, some analysts expect votrient to gain 49% market share overtaking sutent by 2016.
Other analysts predict that the lack of clinical data comparing votrient with other best-selling drugs may turn to be a disadvantage. The ongoing COMPARZ study is expected to help votrient establish its efficacy. The global sales of votrient are expected to grow to around $500m by 2016. The drug generated $60m in global sales in 2010.