Xeljanz XR (tofacitinib citrate) is an 11mg once-daily oral JAK inhibitor developed by Pfizer for the treatment of moderate to severe Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Pfizer submitted the new drug application (NDA) of Xeljanz XR modified release tablets to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for approval on 2 July 2015.
The FDA approved the tablets for the treatment of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis on 24 February 2016.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes and prevalence
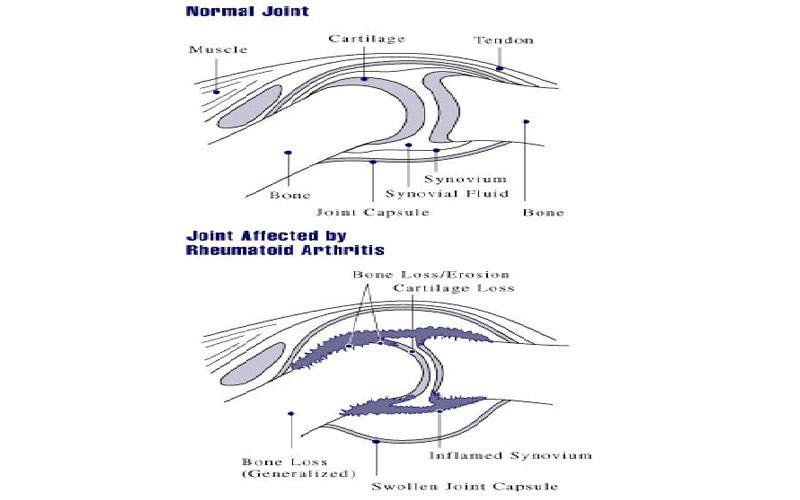
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that results from the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues. It is characterised by inflammation, pain, swelling, stiffness, loss of function and gradual destruction of joints.
RA can affect any joint, but most commonly affects the joints in wrists and fingers, as well as other body parts such as eyes, mouth and lungs. It usually starts in middle age and is most common in older people, more in women than in men.
The defined cause of the disease in unknown, but it is assumed that genes, environment and hormones might be responsible.
Xeljanz XR’s mechanism of action
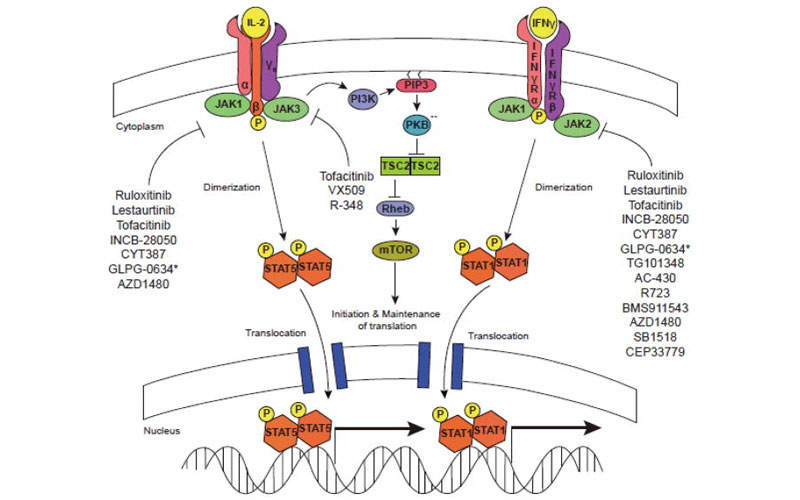
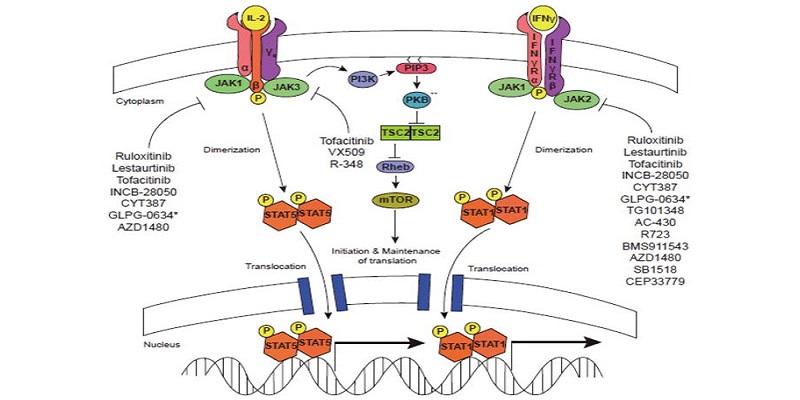
Xeljanz XR is a Janus Kinase inhibitor, which hinders the activity of JAK1, JAK3 and JAK4 enzymes, interfering with the JAK-STAT signalling pathway.
The drug enters the body and binds to the active site of JAK in the cell and inhibits the autophosphorylation and activation of type I, type III and type IV cytokine receptors, which depend upon the JAK family of enzymes for signal transduction.
As a result, the cytokine receptors cannot be phosphorylated and the receptors cannot regulate the JAK-STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) thereby inhibiting the gene transcription and cytokine production.
Clinical trials
The FDA approval of Xeljanz was based on the results obtained from six Phase III clinical trials namely Sync, Standard, Scan, Start, Solo and Step.
Sync is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-centre study that enrolled 792 patients with moderate to severe RA and showed inadequate response to non-biological disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice day or placebo. The primary endpoints of the trial were ACR20 response rate and DAS28-4(ESR) less than 2.6 at month six, and HAQ-DI improvement at month three.
Standard was a similar trial that enrolled 717 patients with moderate to severe RA and showed inadequate response to methotrexate. The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice a day, adalimumab 40mg subcutaneously every other week or placebo along with methotrexate. The primary end points of the trial were ACR20 response rate and DAS28-4(ESR) < 2.6 at month six, and HAQ-DI improvement at month three.
Scan enrolled 797 patients with moderate to severe RA and showed inadequate response to methotrexate. The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice a day or placebo along with methotrexate. The primary endpoints of the trial were ACR20 response, mean change in m-TSS and DAS28-4(ESR) < 2.6 at month six, and HAQ-DI improvement at month three.
Start was a randomised, multi-centre, double-blind, parallel group study. It enrolled 952 patients with active RA and naive to methotrexate. The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice a day or methotrexate. The dosage of methotrexate was started at 10mg/week and increased by 5mg every four weeks as tolerated and to 20mg/week by eight weeks. The primary endpoints at month six were mean change in van der Heijde-mTSS from the baseline and ACR70 response rate.
Solo was a randomised, double-blind, controlled, multi-centre, monotherapy study that enrolled 610 patients with moderate to severe RA and showed inadequate response to non-biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice a day or placebo. The primary endpoints were ACR20 response rate at month 3, HAG-DI improvement and DAS28-4(ESR) < 2.6.
Step enrolled 399 moderate to severe RA patients that showed an inadequate response to TNFi. The patients received Xeljanz 5mg twice a day or 10mg twice a day or placebo along with methotrexate. The primary endpoints at month three were ACR 20 response, HAQ-DI improvement and DAS-4(ESR) < 2.6.