Diabetes occurs when the body cannot regulate its blood glucose levels, impacting the body’s metabolism and how energy is processed and stored. Type 1 and 2 diabetes contribute greatly to the global disease burden, and the number of individuals affected has increased drastically in the past few decades, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form; a person at risk of developing the condition can reduce their chances by limiting certain foods like salt, sugar, and fat, consuming a wider range of foods, including fruits and vegetables, and engaging in regular exercise. However, a novel relationship that has not yet been thoroughly explored, but is more relevant than ever, is the association between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and a new diagnosis of type 1 and 2 diabetes. Zhang and colleagues conducted a systematic review and cohort analysis, published in November 2022 in BMC Medicine, which found that coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) infection increased the likelihood of being newly diagnosed with diabetes, with a higher likelihood of being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, as opposed to type 1.
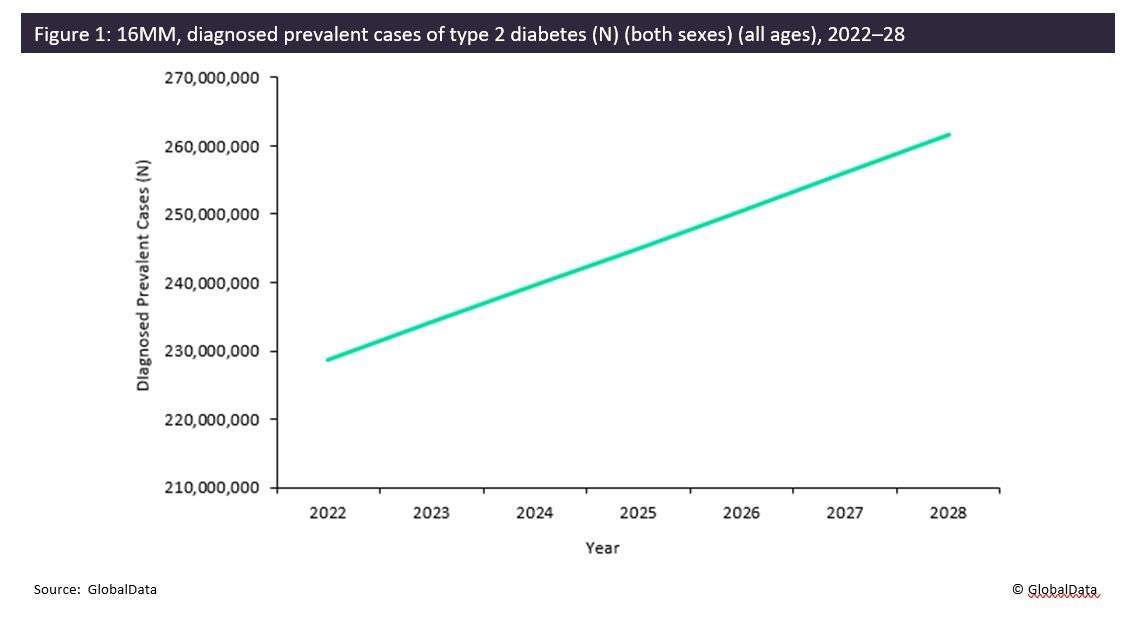
These findings offer valuable insight into how diabetes cases could increase in the future as SARS-CoV-2 continues to cause infections globally, and how the landscape for diabetes prevention could be changed to include Covid-19 infection. GlobalData epidemiologists estimate that by the end of 2022, there will be over 228 million diagnosed prevalent cases of type 2 diabetes in men and women in the 16 major pharmaceutical markets (the US, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the UK, Japan, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, India, Mexico, Russia, South Africa, and South Korea), and that number is set to increase to over 261 million by the end of 2028 (Figure 1).
Zhang and colleagues analysed a total of nine prospective and retrospective cohort studies, totalling a collective sample of 40 million participants, where Covid-19 was the main exposure of interest, had population controls to compare relative associations, and a new diagnosis of diabetes. The meta-analysis found participants post-Covid-19 infection were 1.62 times more likely to develop diabetes overall, 1.48 times more likely to develop type 1 diabetes, and 1.70 times more for type 2 diabetes compared to non-Covid-19-infected participants. Men post-Covid-19 infection were 2.08 times more likely to develop diabetes, and women were 1.99 times more likely, compared to the non-Covid-19 population.
Another factor noted to further increase the risk of diabetes was the length of time post-Covid-19 infection. The risk of diabetes was the highest within the first three months post-Covid-19 infection, and the people who had severe cases of Covid-19 were 1.67 times more likely to develop diabetes, compared to non-Covid-19 participants. Mild to moderate Covid-19 infections were 1.48 time more likely to develop diabetes, compared to non-Covid-19 participants. A statistically significant association between Covid-19 infection and the risk of diabetes was found across all age groups, but those under 18 years of age were at the highest risk. While these results are concerning, additional research is needed to further elaborate on these findings and better understand certain population characteristics that may make a person more or less susceptible to this increased risk of diabetes post-Covid-19 infection.
Better establishing a relationship between Covid-19 and the risk of diabetes contributes to public health knowledge, which helps in developing strategies for prevention and how to best follow-up on Covid-19 infections to reduce the disease burden from diabetes, such as re-enforcing the need for monitoring patients’ glucose metabolism in the post-acute phase of Covid-19.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData