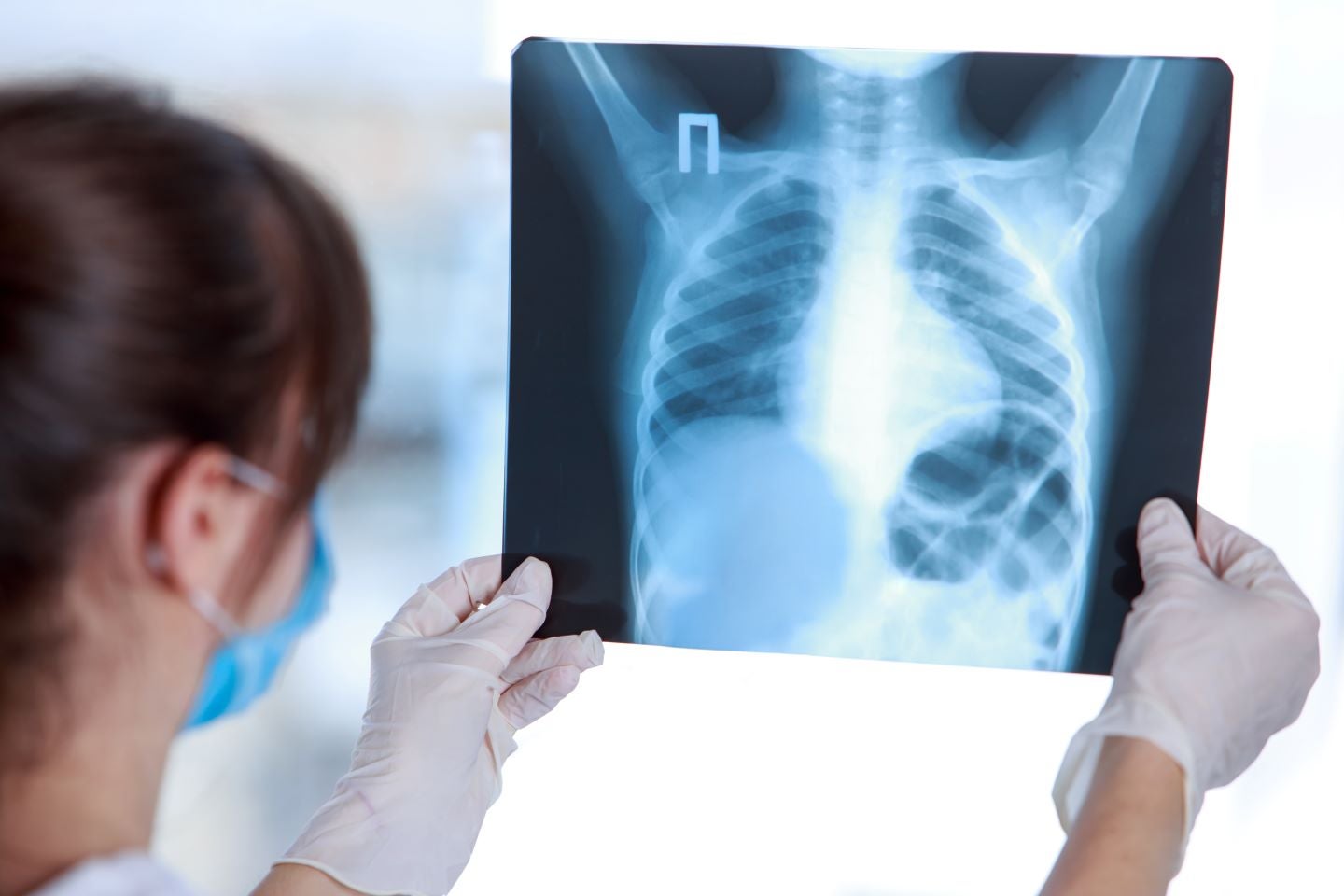
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death, followed by colorectal cancer and liver cancer. Around one-third of cancer deaths are related to lifestyle factors such as tobacco and alcohol consumption, obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. The use of tobacco is strongly associated with lung cancer. According to a study in the UK by Jon Shelton and colleagues that was published in the British Medical Journal in March 2024, lung cancer deaths have declined in both men and women over the last 25 years. This was associated with a sharp decline in the number of smokers in the UK. These findings show the positive impact of increasing public awareness of the harmful effects of smoking.
The study explored the UK cancer incidence and mortality rates for all cancers combined in adults ages 35–69 years. It was a retrospective study that used multiple data sources, such as the Office for National Statistics and the National Health Service and analysed cancer diagnoses and deaths from 1993 to 2018. There were 126,588 cases of all cancers in men in 1993 and 199,848 cases of all cancers in men in 2018. This study reported that all cancer deaths decreased from 1993 to 2018. Moreover, the study also revealed that lung cancer deaths declined by 53.2% in men and 20.7% in women over the last 25 years. The average annual decline in death was 3.1% in males and 2.1% in females. The decline in death was attributed to a historical reduction in smoking rates in both males and females.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
Lung cancer remains a significant health burden in the UK. GlobalData epidemiologists forecast that diagnosed incident cases of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) will increase from 44,000 cases in 2024 to around 50,000 cases in 2032. This increase in cases is driven by the underlying population age structures and population growth rather than an actual increase in lung cancer incidence. According to Cancer Research UK, lung cancer incidence has steadily declined, coinciding with the general trend of a decrease in smoking rates in the population.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide. Lung cancer is usually diagnosed at advanced stages with a poor prognosis. Cigarette smoking accounts for 85% of all lung cancer, and smoking cessation dramatically reduces the risk of lung cancer in the population. The UK has implemented various tools such as an increase in taxes, the prohibition of smoking in public places, and smoking cessation clinics to reduce the number of smokers. The outcome of these interventions has been positive. However, vaping (smoking an electronic cigarette) is increasing among teenagers, which will increase the risk of lung cancer in the future. The UK should continue to promote healthy choices and discourage smoking in various forms including electronic cigarettes.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData