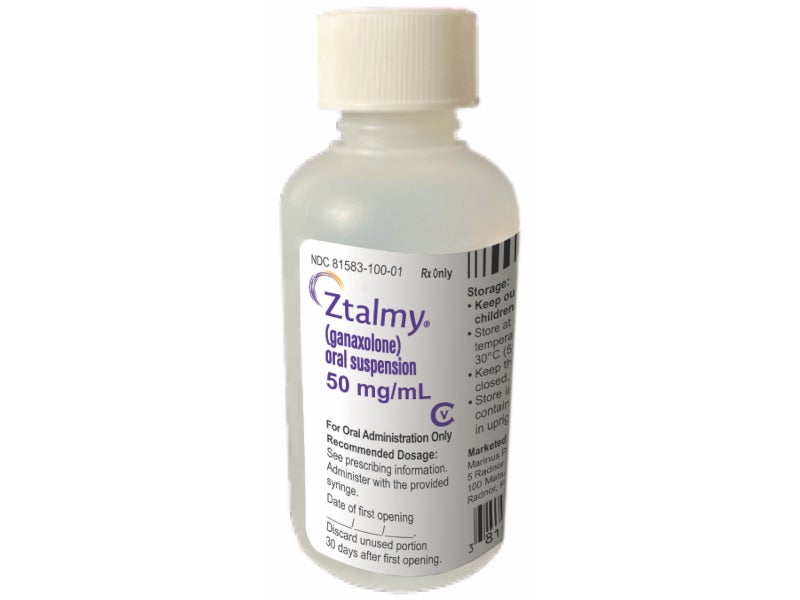
ZTALMY® (ganaxolone) is indicated for the treatment of seizures associated with a rare, genetic epilepsy known as cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDLK5) deficiency disorder (CDD) in patients aged two years and older.
Developed by US-based pharmaceutical company Marinus Pharmaceuticals, the drug is available as an oral suspension of 50mg/ml ganaxolone, with each bottle containing 110ml of sugar-free, off-white cherry-flavoured oral solution.
In August 2021, Orion collaborated with Marinus to obtain exclusive rights for marketing both oral and intravenous (IV) dose formulations of ganaxolone in the European Economic Area, the UK and Switzerland for CDD, tuberous sclerosis complex and refractory status epilepticus.
In October 2022, Marinus entered into a revenue interest financing agreement with Sagard Healthcare Partners, a biopharmaceutical royalties investment unit of the capital market company Sagard, for $32.5m upfront in return for payments based on the net sales of ganaxolone, including ZTALMY oral suspension CV, in the US.
Marinus collaborated with Tenacia Biotechnology, a biotechnology company based in China, for the development and commercialisation of ganaxolone in China in November 2022.
Regulatory approvals for ZTALMY
ZTALMY received orphan drug and rare paediatric disease designations from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2017 and July 2020 respectively for the treatment of CDD.
The European Medical Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products granted orphan drug designation to ganaxolone for the treatment of CDD in November 2019.
In August 2021, the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) granted Marinus’ request for an accelerated assessment of ganaxolone for the treatment of seizures associated with CDD.
In July 2021, Marinus submitted a new drug application for the use of ganaxolone for the treatment of seizures associated with CDD. The FDA accepted the application for priority review in September 2021 and approved the drug for the condition in March 2022.
ZTALMY oral suspension CV was commercially launched in the US in July 2022.
The EMA’s CHMP recommended ZTALMY for the adjunctive treatment of epileptic seizures associated with CDD in patients aged two to 17 years in May 2023.
In July 2023, ZTALMY became the first approved treatment in Europe for seizures associated with CDD in children and adolescents and may be continued in patients aged 18 years and older.
CDKL5 deficiency disorder signs and symptoms
CDD is a rare refractory form of paediatric epilepsy characterised by early‑onset, difficult‑to‑control seizures and severe neuro‑developmental impairment. It is caused by a mutation of the CDKL5 gene, which is located on the X chromosome and produces a protein that is crucial for normal brain development and functioning.
Common identifiable symptoms of the condition include early-onset epileptic seizures, limited hand and walking skills, an inability to talk, poor eye contact (cortical visual impairment), constipation, sleep issues, stereoscopic hand motions (stereotypies), teeth-grinding (bruxism), inadequate muscle tone (hypotonia) and intellectual inability.
The condition affects approximately one individual in 40,000 live births, predominantly females.
ZTALMY’s mechanism of action
ZTALMY is a neuroactive steroid anticonvulsant that works as a positive allosteric modulator of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA-A) receptor in the CNS.
The drug’s precise mechanism and therapeutic effects in reducing seizures are unknown, but its anticonvulsant effects are thought to result from positive allosteric modulation of the GABA-A receptor.
Enhanced activity of GABA (an inhibitory neurotransmitter) in the brain is believed to reduce seizures.
Clinical trials on ZTALMY
The approval of ZTALMY was based on results from a global, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled Phase III clinical trial named Marigold.
The study evaluated ZTALMY’s effectiveness in treating seizures associated with CDD in patients aged two years and older. A total of 101 patients were randomised to receive either ZTALMY or placebo. The study’s primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage reduction in major motor seizure frequency in CDD patients on day 28.
Patients treated with ZTALMY showed a median reduction of 30.7% in the frequency of major motor seizures, compared to a median 6.9% reduction for those receiving a placebo at day 28.
In the Marigold open-label extension study, patients treated with ZTALMY for at least a year achieved a 49.6% median reduction in major motor seizure frequency. The most common side effects in the clinical trial were somnolence (sleepiness), pyrexia (fever), salivary hypersecretion, and seasonal allergies.
Additional studies on ZTALMY
The company is continuously investing in the potential of ganaxolone in IV and oral formulations to improve the therapeutic reach of the drug for adult and paediatric patients in acute and chronic care settings.
In 2021, Marinus began an open-label Phase II clinical trial named CALM to evaluate the effectiveness, safety and tolerability of adjunctive oral ganaxolone treatment in patients with seizures associated with TSC.
A Phase II Researching Established Status Epilepticus Treatment (RESET) study is being conducted to study the effects of adjunctive IV ganaxolone in established status epilepticus (ESE) patients.
A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial named Randomised Therapy In Status Epilepticus (RAISE) is being conducted in the US to evaluate the efficacy and safety of IV ganaxolone in patients with RSE.
The trial is being funded in part by the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority which is part of the Administration for Strategic Preparedness and Response at the US Department of Health and Human Services.
A Phase III randomised, placebo-controlled RAISE II clinical trial has been planned to evaluate the safety and efficacy of IV ganaxolone along with the standard of care for the treatment of RSE.
In December 2021, Marinus collaborated with the Loulou Foundation and six other biotech and pharmaceutical organisations to undertake the Clinical Assessment of NeuroDevelopmental measures In CDD (CANDID) study, a three-year observational study in CDD patients.
Loulou Foundation, a private non-profit organisation focused on developing treatments for seizure disorders, will coordinate the clinical study, which will be conducted in CDD clinical centres worldwide.